
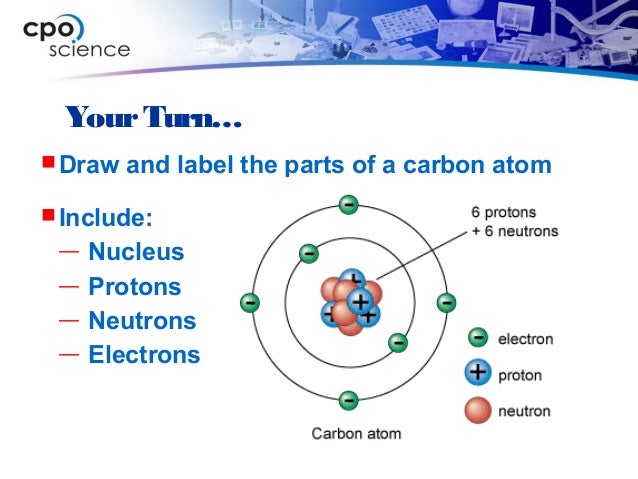
When the electrons are excited, they can transfer between the shells. The number of maximum electrons that can occupy one shell is defined by the formula of 2nî or 2n square, where n is the number of the shell. The first level contains only 2 electrons. These levels may be designated K L M N shells (or 1 2 3 4 orbits). In accordance with the Bohr Model, electrons are considered to move around the nucleus in fixed shells (orbits), at various energy levels. Tritium is an unstable isotope of hydrogen. And isotopes that can decay during a defined period are called unstable (or radioactive) isotopes.Ītomic Structure of isotopes of Hydrogen 1 2 3 Isotopes that cannot decay during a defined period are called stable isotopes. The same element can exist in different forms, each form having the sameĪtomic number, but different mass numbers. If the number of electrons is changed the atom will become ionizedĪnd gain either a positive (fewer electrons) In a stable uncharged atom the number of electrons will equal the number of protons. Atomic Weight = number of protons + number of neutrons There are 94 naturally occurring elements (1-94)Īnd others which have been artificially created (95+.)Įach element has an Atomic Weight for the most commonly found isotope. Each unique element has an Atomic Number equal to the number of protons it contains. Orbiting around the nucleus are the electrons. The nucleus, in the center of an atom, consists of protons and neutrons.
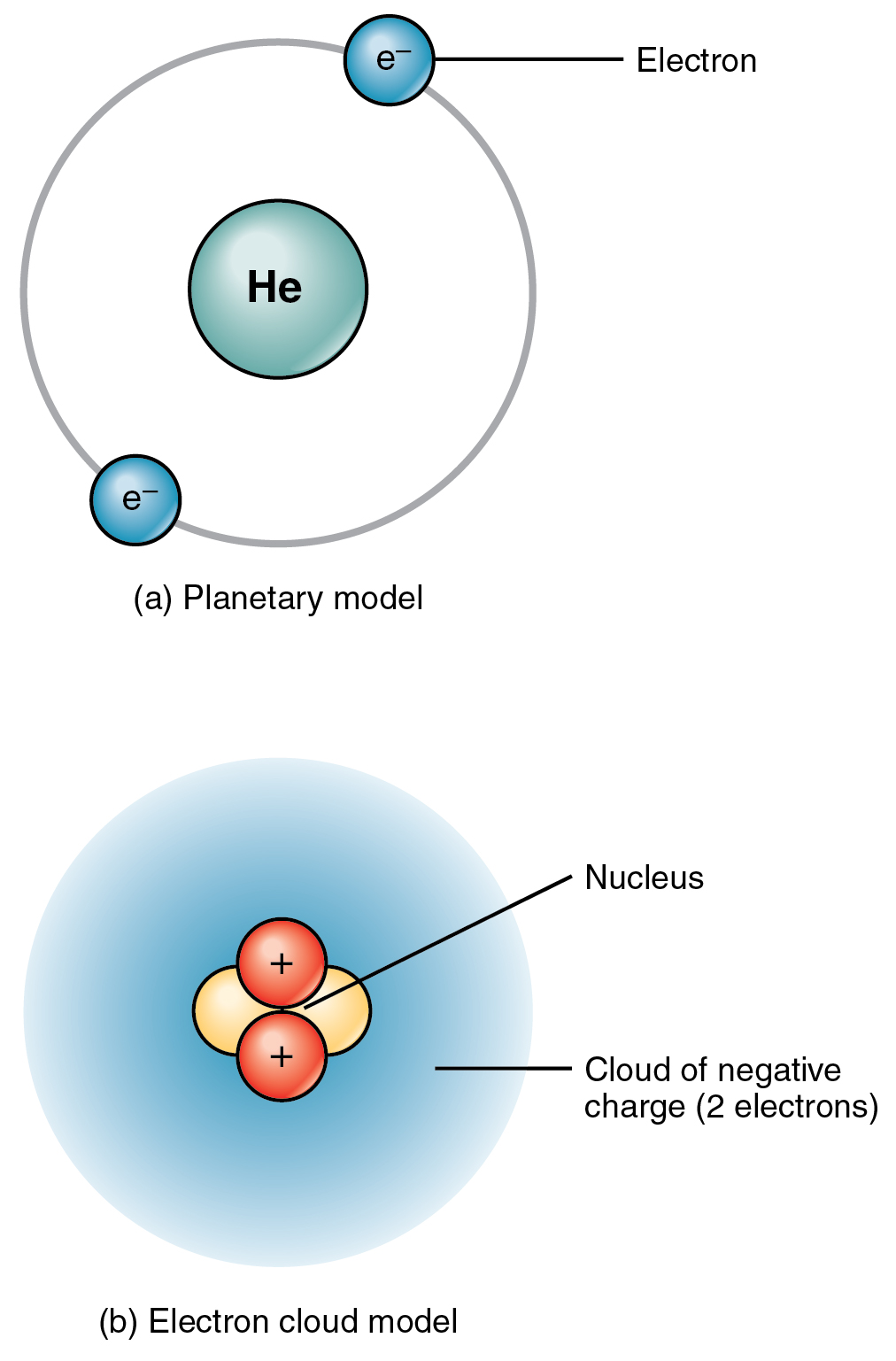
Model of a Lithium atom Atomic Structure The Nucleus, in the center of the atom, consists of protons and neutrons. It is made up of three subatomic structures called Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons. An Atom is a small part of an element that takes part in chemical reactions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
